|
 |
 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Confocal Microscopy Image Gallery
Embryonic Rat Thoracic Aorta Medial Layer Myoblast Cells (A-10 Line)
The morphology of A-10 cells is similar to that of myoblasts, the precursors of muscle fibers. In culture, the cells grow adherently and generate spontaneous action potentials at the stationary phase of the growth cycle. An increase in activity of the enzymes myokinase and creatine phosphokinase in the cells has been documented.

The clonal A-10 line was established form the thoracic aorta of a DB1X strain embryonic rat (Rattus norvegicus). A branch of the descending aorta, the thoracic aorta extends from the aortic arch to the diaphragm. Facilitating the transportation of blood from the heart to the other regions of the body is the primary function of the thoracic aorta.
Due to the possible involvement of muscle cells in a variety of health problems, the A-10 cell line is commonly utilized in experiments carried out in medical research laboratories. One area of particular interest in recent years has been the possible link between increased smooth muscle cell sizes and numbers and hypertension. Some studies suggest that unusually large or numerous muscle cells present in the walls of the arteries can inhibit blood flow due to constriction of the lumenal space. Theoretically, such increased resistance to blood flow would cause a corresponding increase in blood pressure, as the cardiovascular system attempts to counteract the change so that adequate quantities of blood can continue to reach all bodily tissues.
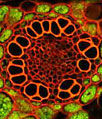
A semi-confluent culture of A-10 cells (illustrated above) was fixed, permeabilized, and blocked with 10-percent normal goat serum in phosphate-buffered saline prior to immunofluorescent labeling with primary antibodies to giantin, a protein resident in the Golgi complex of mammalian cells. The culture was subsequently stained with a mixture of secondary antibodies conjugated to Alexa Fluor 568 in a mixture containing phalloidin conjugated to Alexa Fluor 488 (pseudocolored blue). The cell nuclei were counterstained with the red-absorbing dye TO-PRO-3 (pseudocolored green). Images were recorded with a 60x oil immersion objective using a zoom factor of 3.0 and sequential scanning with the 488-nanometer spectral line of an argon-ion laser, the 543-nanometer line from a green helium-neon laser, and the 633-nanometer line of a red helium-neon laser. During the processing stage, individual image channels were pseudocolored with RGB values corresponding to each of the fluorophore emission spectral profiles unless otherwise noted above.
Additional Confocal Images of Embryonic Rat Thoracic Aorta (A-10) Cells
Labeling A-10 Cells for Focal Adhesions with Immunofluorescence - The culture of A-10 myoblasts featured in this section was immunofluorescently labeled with anti-vinculin mouse monoclonal primary antibodies followed by goat anti-mouse IgG secondary antibodies conjugated to Alexa Fluor 647 (pseudocolored blue). In addition, the specimen was stained for DNA with the ultraviolet-absorbing probe Hoechst 33342 (pseudocolored cyan), for the cytoskeletal filamentous actin network with Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated to phalloidin, and for mitochondria with MitoTracker Red CMXRos.
Mitochondria, Actin, and DNA Distribution in A-10 Myoblasts - The embryonic rat thoracic aorta (A-10) cells presented in this section were resident in an adherent culture stained for F-actin with BODIPY FL conjugated to phallacidin, and for DNA with the red-absorbing dye TO-PRO-3. The culture was also labeled with MitoTracker Orange CMTMRos, targeting the mitochondrial network.
Targeting the Golgi Complex in Rat Thoracic Aorta Cells - In this section, a culture of embryonic rat thoracic aorta (A-10) cells is illustrated that was fixed with paraformaldehyde, permeabilized, and treated with rabbit (anti-giantin) primary antibodies, followed by secondary antibodies conjugated to Alexa Fluor 568, targeting the Golgi apparatus. DNA in the cell nucleus was counterstained with TO-PRO-3 (pseudocolored cyan).
Imaging the Mitochondrial and F-Actin Networks in Monolayer Thoracic Aorta Cell Cultures - A monolayer culture of A-10 myoblasts was treated with MitoTracker Red CMXRos in medium containing 15 percent Cosmic calf serum, fixed with the same medium containing 3.7 percent paraformaldehyde, permeabilized with 0.2 percent Triton X-100, and then counterstained with TO-PRO-3 (pseudocolored blue), targeting DNA in the nuclei. In addition, the filamentous actin network was labeled with Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated to phalloidin.
A-10 Cells with MitoTracker Deep Red 633, Alexa Fluor 488, and SYTOX Orange - A triple fluorophore combination of MitoTracker Deep Red 633, Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated to phalloidin, and SYTOX Orange was used to label an adherent log phase culture of A-10 cells for mitochondria, the filamentous actin network, and nuclear DNA, respectively. The cells were first treated with MitoTracker Deep Red 633 in growth medium for one hour, washed and fixed with paraformaldehyde (prepared in growth medium), permeabilized, and blocked with bovine serum albumen. The cells were subsequently labeled with the conjugated phalloidin and counterstained with the SYTOX reagent.
Proximity of Filamentous Actin and Mitochondrial Networks in Embryonic Rat Aorta Cells - An adherent monolayer A-10 cell culture was labeled for the cytoskeletal filamentous actin and intracellular mitochondrial networks with Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated to phalloidin and MitoTracker Red CMXRos, respectively. Nuclei present in the myoblasts were counterstained with the far-red fluorescent DNA-probe DRAQ 5.
A-10 Myoblast Culture Immunofluorescently Labeled for Vinculin - Vinculin, a protein associated with focal adhesion and adherens junctions, was immunofluorescently targeted in a culture of embryonic rat thoracic aorta cells with anti-vinculin mouse monoclonal primary antibodies followed by goat anti-mouse Fab heavy and light chain fragments conjugated to Alexa Fluor 647 (pseudocolored red). In addition, the specimen was stained for mitochondria with MitoTracker Red CMXRos (pseudocolored yellow) and for F-actin with Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated to phalloidin. Cell nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst 33342, which emits blue fluorescence when bound to dsDNA.
Contributing Authors
Nathan S. Claxton, Shannon H. Neaves, and Michael W. Davidson - National High Magnetic Field Laboratory, 1800 East Paul Dirac Dr., The Florida State University, Tallahassee, Florida, 32310.