|
 |
 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Confocal Microscopy Image Gallery
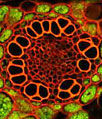
Swallowtail Butterfly Visual Interneurons
Visual interneurons obtained from the beautiful swallowtail butterfly were injected with the fluorochrome Lucifer yellow in order to capture the image illustrated below. The specimen was imaged with extended focus in 100-micrometer serial sections through the 383-micrometer axial range of the specimen and displayed in an overlapping pseudo coloring scheme. The image was provided by Mituyo Kinoshita and Kentaro Arikawa from the Laboratory of Neuroethology in the Graduate School of Integrated Science at the Yokohama City University, in Japan.

Swallowtail butterflies are members of the insect subfamily Papilioninae and are well known for the characteristic tail-like extensions that appear on their hindwings. Among the most visually stunning creatures on Earth, swallowtails display a wide variety of colors and markings. Perhaps the most easily identified is the zebra swallowtail, which features a striped pattern similar to that of its mammal namesake and is frequently seen flying close to the ground in North America and many other locales. Especially abundant near wooded streams, swamps, and marshes, members of the species possess shorter tongues than many other large butterflies and, therefore, typically only visit daisies and other flat-topped flowers to sip nectar.
As illustrated above, the swallowtail butterfly is also beautiful at the microscopic level and, more importantly, such examination can reveal important scientific information. The confocal microscopy technique, which offers controllable depth of field and elimination of the out-of-focus information that can frequently degrade images, is especially advantageous for the close study of minute structures such as the visual interneurons, nerve cells that act as a link between sensory and motor neurons. Fluorescent labeling provides positional information and enables identification of various cellular components, while optical sectioning can be utilized to reconstruct remarkable three-dimensional images.