 |
 |
 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Confocal Microscopy Image Gallery
Retina Ganglion Cell
Vividly stained with the fluorochrome Lucifer yellow, the retina ganglion cell in the central portion of the image below is extruding a multiple of processes. Closely associated dopamine-operated amacrine cells were counterstained with Texas Red. The confocal image was provided by Professor Shigetada Nakanishi of the Department of Biological Sciences at the Kyoto University Faculty of Medicine in Japan.
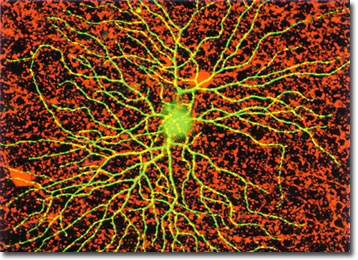
The retina, which is composed of a thin layer of tissue lining the rear interior portion of the eye, is responsible for gathering optical signals received through the lens and pre-processing the information before sending it onto higher visual centers in the brain. As such, the retina acts in an optical sense as a multifaceted filter to segregate temporal, spatial, and chromatic aspects of the visual signal. A hierarchy of organization exists within the many layers of cells interconnected throughout the retina, which is composed of more than 60 individual neuron classes. Ganglion cells are located in one of the innermost layers of the retina, and act as an output buffer to code and compress electrical signals into a sequence of action potentials that pass through the optic nerve.
Confocal microscopy is a powerful tool for investigating the intricate structural and functional features of neurons and supporting cells in a variety of brain tissues. For example, using a variety of fluorescent probes, investigators have successfully labeled presynaptic terminals in the retinas of a broad range of animals, including amphibians, mammals, fish, and turtles. The pattern of dye uptake can be studied in live retinal preparations to examine the distribution to rod and cone cells, as well as bipolar, amacrine, horizontal, and ganglion cells throughout the retinal tissue. In addition, the optical sectioning capability of confocal microscopy can be employed to reconstruct three-dimensional images illustrating the anatomy of neural cells in the retina.
